The stratosphere has a powerful impact on the weather we experience every day
STRIVE Provides a Comprehensive Perspective on Atmospheric Processes
STRIVE’s observations provide the missing pieces needed to improve our understanding of stratosphere-troposphere interactions and their impact on the ozone layer, weather, and air quality.
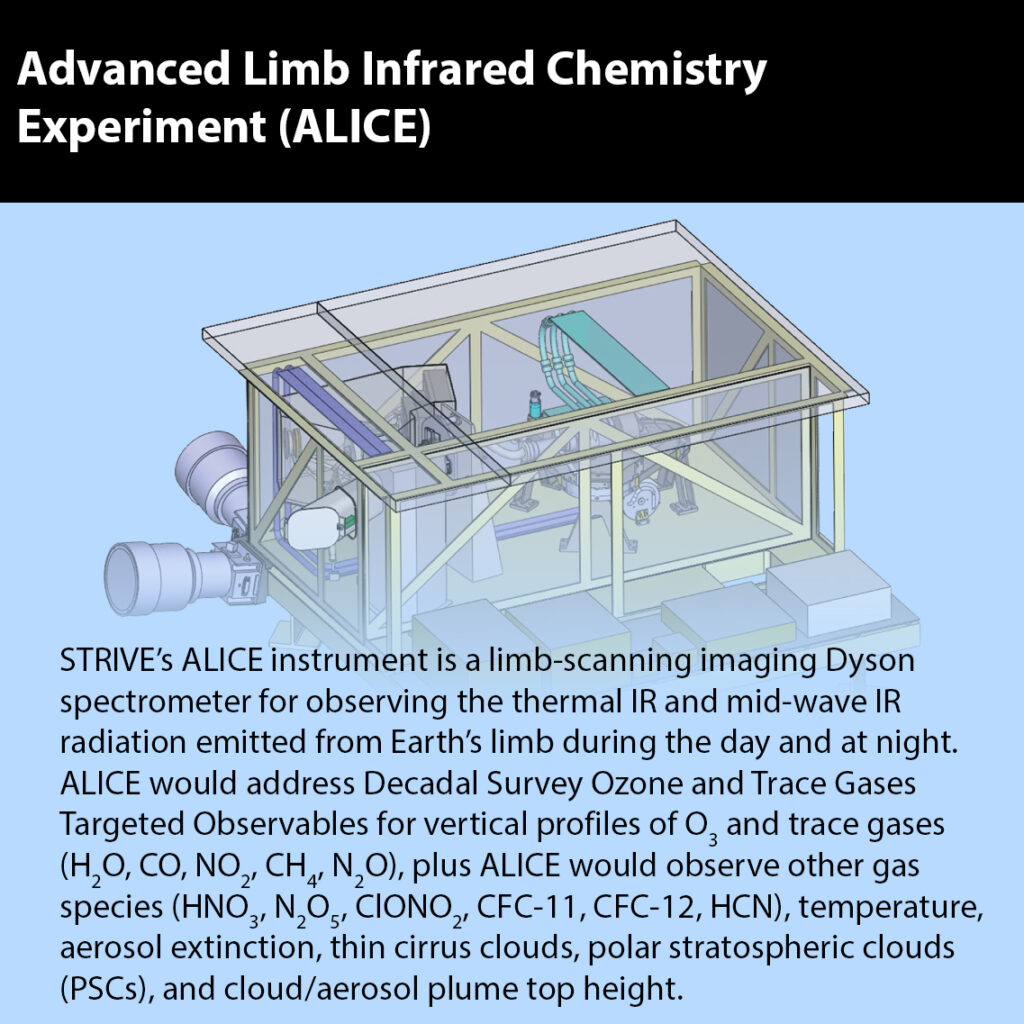
STRIVE has two advanced limb-viewing instruments, Advanced Limb Infrared Chemistry Experiment (ALICE) and Aerosol Radiometer for Global Observations of the Stratosphere (ARGOS). Working together, ALICE and ARGOS measure temperature, ozone, trace gases, aerosols, and clouds, providing a comprehensive view of atmospheric processes in the upper troposphere and stratosphere.
The instruments use a limb-viewing geometry, measuring radiation along a slanted path near Earth’s horizon. Limb-viewing enhances vertical resolution, capturing fine-scale structures with greater sensitivity to trace gases, aerosols, and thin clouds compared to nadir observations. STRIVE also leverages advancements in imaging detectors, cryocoolers and compact optics, and novel instrument design to achieve significantly improved spatial resolution and global sampling over previous limb sounders.



High Heritage Provides Capability and Flexibility
STRIVE launches into a Sun-synchronous orbit that enables near-global coverage from 82oN to 82oS over its three-year mission. The observatory is a high-heritage Northrop Grumman (NG) spacecraft, which provides the precise pointing control needed to enable groundbreaking observations. ALICE’s onboard capability to adjust pixel-binning and averaging allows for operational flexibility. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) builds the ALICE instrument, with BAE SMS providing the focal plane assembly, cryocooler, and associated electronics. Quantum Space (QS), in collaboration with Science Systems and Applications, Inc (SSAI) contributes the ARGOS instrument.
STRIVE leverages NG’s existing Mission Control Complex, which has supported 45+ successful missions. ALICE data processing and distribution are handled by an established National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) facility, which processed the heritage HIRDLS data and currently supports MOPITT. ARGOS data processing is provided by QS, leveraging GSFC OMPS-LP data processing heritage.