Cross-spectral analysis Nino3.4 vs. North Pacific Index
Contents
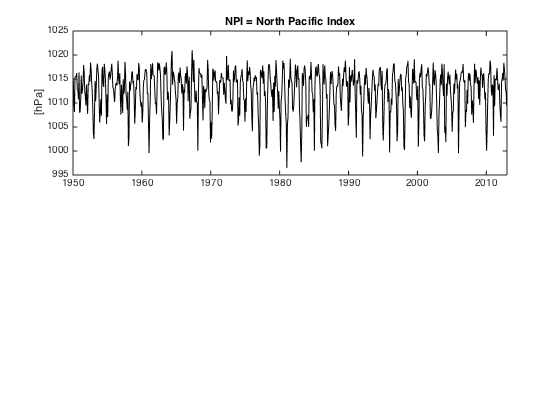
Plot sea-surface temperature and NPI anomalies
load SSTA;
N = length(yr);
Nyr = round(N/12);
NPdat = load('NPindex_monthly.txt');
yyyymm = NPdat(:,1);
post1950 = (yyyymm>195000);
pre2013 = (yyyymm<201300);
NPI = NPdat(post1950&pre2013,2);
figure(1)
clf
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(yr,NPI,'k')
ylabel('[hPa]')
title('NPI = North Pacific Index')
xlim([1950 2013])
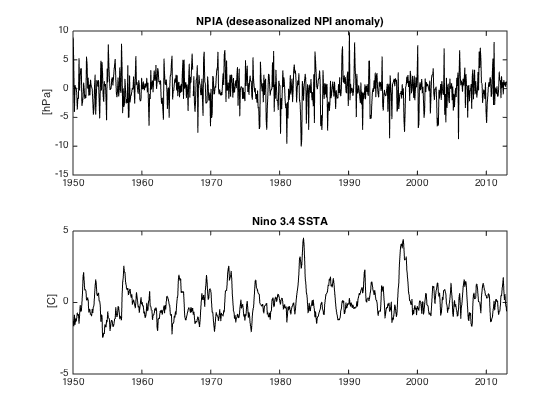
Deseasonalize to get NPIA; compare with Nino 3.4 SSTA
NPIhat = fft(NPI);
NPIAhat = NPIhat;
filtindex = [1 + (0:3)*Nyr N+1 - (1:3)*Nyr];
NPIAhat(filtindex) = 0;
NPIA = real(ifft(NPIAhat));
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(yr,NPIA,'k')
ylabel('[hPa]')
title('NPIA (deseasonalized NPI anomaly)')
xlim([1950 2013])
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(yr,SSTA,'k')
ylabel('[C]')
title('Nino 3.4 SSTA')
xlim([1950 2013])
ylim([-5 5])
Are SSTA and NPIA correlated?
R = corrcoef(NPIA,SSTA);
R_SSTA_NPIA = R(1,2)
R_SSTA_NPIA =
-0.1707
One-sided spectra/cross spectra
Nwyr = 20;
rate = 12;
Nw = Nwyr*rate;
df = 1/Nwyr;
fn = rate/2;
[Pxy,f]=cpsd(SSTA,NPIA,hann(Nw),Nw/2,Nw,rate);
[Pxx,f]=pwelch(SSTA,hann(Nw),Nw/2,Nw,rate);
[Pyy,f]=pwelch(NPIA,hann(Nw),Nw/2,Nw,rate);
Cohxy = Pxy./sqrt(Pxx.*Pyy);
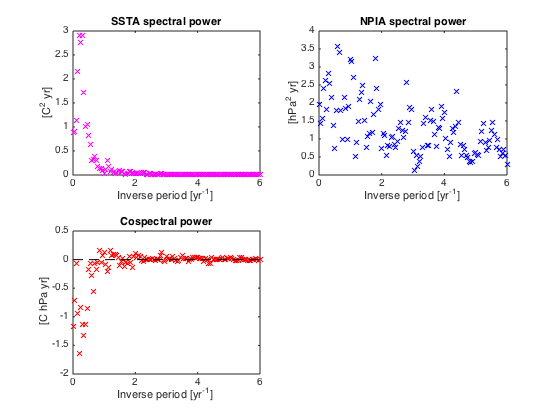
Plot the windowed power spectra of SSTA and NPIA and their cospectrum
figure(2)
clf
subplot(221)
plot(f,real(Pxx),'mx')
xlim([0 fn])
xlabel('Inverse period [yr^{-1}]')
ylabel('[C^2 yr]')
title('SSTA spectral power')
subplot(222)
plot(f,real(Pyy),'bx')
xlim([0 fn])
xlabel('Inverse period [yr^{-1}]')
ylabel('[hPa^2 yr]')
title('NPIA spectral power')
subplot(223)
plot(f,real(Pxy),'rx',[0 max(f)],[0 0],'k--')
xlim([0 fn])
xlabel('Inverse period [yr^{-1}]')
ylabel('[C hPa yr]')
title('Cospectral power')
Frequency partitioning of covariance
cov12 = cov(SSTA,NPIA);
cov_SSTA_NPIA = cov12(1,2)
covWinFreqIntegral_SSTA_NPIA =sum(real(Pxy)*df)
cov_SSTA_NPIA =
-0.5093
covWinFreqIntegral_SSTA_NPIA =
-0.5169
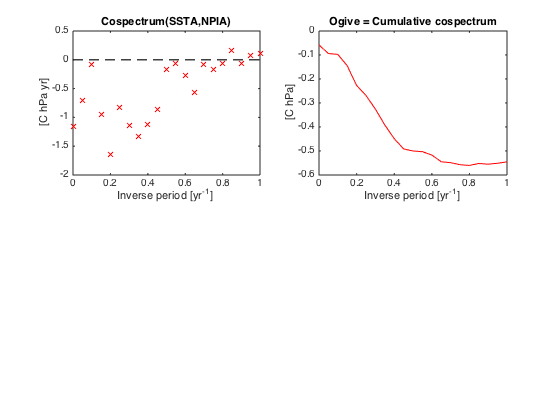
Replot cospectrum including only subannual frequencies; plot ogive
figure(3)
clf
subplot(221)
plot(f,real(Pxy),'rx',[0 max(f)],[0 0],'k--')
xlim([0 1])
xlabel('Inverse period [yr^{-1}]')
ylabel(' [C hPa yr] ')
title('Cospectrum(SSTA,NPIA)')
subplot(222)
plot(f,cumsum(Pxy*df),'r-')
xlim([0 1])
xlabel('Inverse period [yr^{-1}]')
ylabel('[C hPa]')
title('Ogive = Cumulative cospectrum')
Warning: Imaginary parts of complex X and/or Y arguments ignored
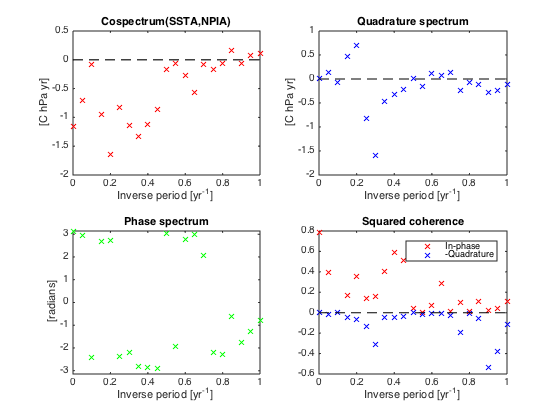
Quadrature spectrum, phase and magnitude-squared coherence
subplot(222)
plot(f,imag(Pxy),'bx',[0 max(f)],[0 0],'k--')
xlim([0 1])
xlabel('Inverse period [yr^{-1}]')
ylabel(' [C hPa yr] ')
title('Quadrature spectrum')
subplot(223)
plot(f,angle(Pxy),'gx')
xlim([0 1])
ylim([-pi pi])
xlabel('Inverse period [yr^{-1}]')
ylabel(' [radians] ')
title('Phase spectrum')
subplot(224)
plot(f,real(Cohxy).^2,'rx',f,-imag(Cohxy).^2,'bx',[0 max(f)],[0 0],'k--')
xlim([0 1])
xlabel('Inverse period [yr^{-1}]')
title('Squared coherence')
legend('In-phase','-Quadrature')
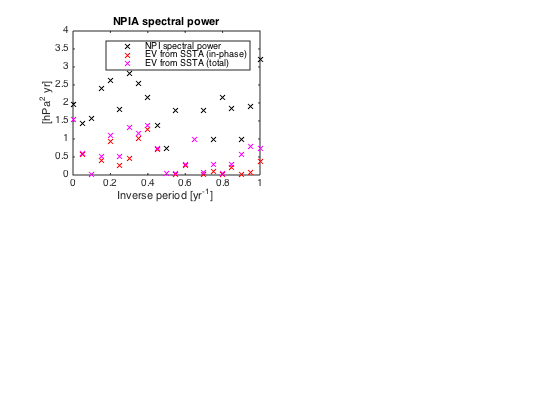
Variance of NPI explained by SSTA
figure(4)
clf
subplot(221)
plot(f,real(Pyy),'kx')
xlim([0 1])
xlabel('Inverse period [yr^{-1}]')
ylabel('[hPa^2 yr]')
title('NPIA spectral power')
hold on
plot(f,real(Pyy).*real(Cohxy).^2,'rx',f,real(Pyy).*abs(Cohxy).^2,'mx')
legend('NPI spectral power','EV from SSTA (in-phase)','EV from SSTA (total)')
hold off