Windowed Fourier analysis of a musical sample
We use windowed DFTs to break a short segment of Handel's Messiah into its time-varying component frequencies, which are the musical notes being sung and their overtones. This is called a spectrogram.
Contents
- Load data and see what we have
- Plot the data
- Play the data as music
- DFT power spectra using Hann window
- Use Matlab spectrogram function to make the same plot
- Replot with frequency in octaves from concert A = 440 Hz
- Block-average S from Nav adjacent overlapping windows, then replot
- Figure 2: Zoom in on first second and two octaves and pick out notes
Load data and see what we have
load handel %this music dataset is built into Matlab who Fs % Sampling frequency (samples/sec) Ny = length(y) % Number of samples in the segment
Your variables are:
Fs y
Fs =
8192
Ny =
73113
Plot the data
figure(1) clf subplot(2,1,1) plot((1:Ny)/Fs,y); xlabel('Time [s]'); ylabel('Sound pressure'); title('Music time series');

Play the data as music
p8 = audioplayer(y,Fs); playblocking(p8);
DFT power spectra using Hann window
Nw = 256; j = 1:Nw; w = 0.5*(1-cos(2*pi*(j-1)/Nw))'; % Hanning window of length Nw: % SP toolbox: w=hanning(Nw,'periodic') varw = 3/8; % Mean-square value of taper function w (used to % renormalize power spectrum). % Segment the data into 'full' and 'half' windows, arrayed in columns nwinf = floor(Ny/Nw); % Number of 'full' windows starting each Nw samples nwinh = nwinf - 1; % Number of 'half' windows (half-way between fulls) nwin = nwinf+nwinh; yw = zeros(Nw,nwin); % Define array in which to insert windowed data yw(:,1:2:nwin) = reshape(y(1:nwinf*Nw),Nw,nwinf); yw(:,2:2:(nwin-1)) = reshape(y((1+Nw/2):(nwinf-0.5)*Nw),Nw,nwinh); % Taper each column (i. e. the data in each window) wmx = repmat(w,[1 nwin]); yt = wmx.*yw; % DFT and power spectrum of each column ythat = fft(yt); S = (abs(ythat/Nw).^2)/varw; %Windowed power spectrum S = S(1:Nw/2,:); % Only keep nonnegative harmonics for plotting SdB = 10*log10(S); % log of spectrum in decibel-like units Mw = 0:(Nw/2 - 1); % Nonnegative windowed harmonics fw = Fs*Mw/Nw; % "Frequencies'(inverse periods in Hz) of these harmonics tw = (1:nwin)*0.5*Nw/Fs; % Center time of each window % Plot the power spectra (log or decibel scale) vs. window time subplot(2,1,2) % Add offsets and padding so pcolor centers each cell on (tw,fw) % and last row/col of field is included in plots dfw = fw(2)-fw(1); dtw = tw(2)-tw(1); fwpad = [fw fw(end)+dfw]-0.5*dfw; twpad = [tw tw(end)+dtw]-0.5*dtw; SdBpad = SdB([1:end end],[1:end end]); pcolor(twpad,fwpad,SdBpad) xlabel('time [s]') ylabel('Frequency [Hz]') title('Windowed spectral power of Messiah sample') shading flat colorbar

Use Matlab spectrogram function to make the same plot
[ywinhat,fw2,t2,P2] = spectrogram(y,hann(Nw,'periodic'),Nw/2,Nw,Fs); % Convert 1-sided power spectral density P2 (in power per Hz) % into two sided periodogram (in power per FFT frequency S2 = P2*Fs/Nw; SdB2 = 10*log10(S2); % Convert spectral power to decibel scale subplot(2,1,1) image(t2,fw2,SdB2,'CDataMapping','scaled') %CDataMapping=scaled % uses the range of values of SdB2 to make the color scale. axis xy % Puts low frequencies at the bottom colorbar
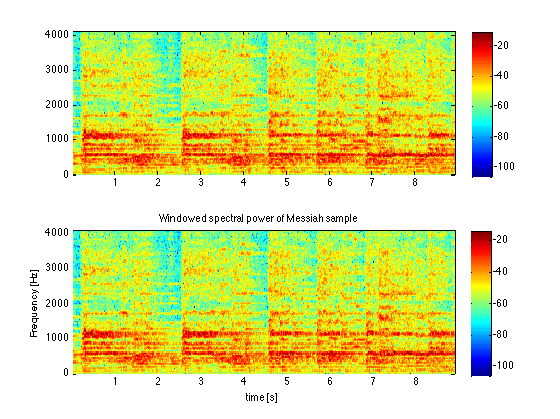
Replot with frequency in octaves from concert A = 440 Hz
% Plot log2(freq) = octaves, but have to exclude m=1 (zero freq) pcolor(twpad,log2(fwpad(2:end)/440),SdBpad(2:end,:)) caxis([-40 -10]) xlabel('time [s]') ylabel('octaves above concert A (440 Hz)') title('Windowed spectral power of Messiah sample') shading flat colorbar
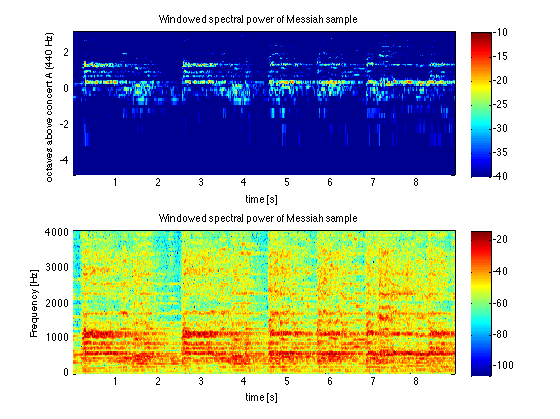
Block-average S from Nav adjacent overlapping windows, then replot
Nav = 4; % Number of overlapping windows used for averaging spectra ntav = floor(nwin/Nav); nwininav = ntav*Nav; % Note use of reshape for computationally efficient block averaging twav = mean(reshape(tw(1:nwininav),Nav,ntav)); % Average times Sav = reshape(S(:,(1:nwininav)),Nw/2,Nav,ntav); Sav = mean(Sav,2); Sav = squeeze(Sav); % Now Nw/2 x ntav SavdB = 10*log10(Sav); dtwav = twav(2)-twav(1); twavpad = [twav twav(end)+dtwav]-0.5*dtwav; SavdBpad = SavdB([1:end end],[1:end end]); pcolor(twavpad,log2(fwpad(2:end)/440),SavdBpad(2:end,:)) caxis([-40 -10]) xlabel('time [s]') ylabel('octaves above concert A (440 Hz)') title(['Windowed spectral power [dB],' int2str(Nav) '-spectrum avg']) shading flat colorbar

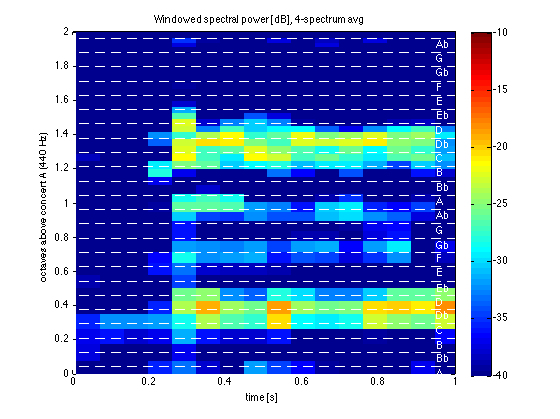
Figure 2: Zoom in on first second and two octaves and pick out notes
figure(2) clf % Make same block-avg windowed power spectrum plot as above... pcolor(twav-0.5*dtwav,log2((fw(2:end)-0.5*dfw)/440),SavdB(2:end,:)) caxis([-40 -10]) xlabel('time [s]') ylabel('octaves above concert A (440 Hz)') title(['Windowed spectral power [dB], ' int2str(Nav) '-spectrum avg']) shading flat colorbar % Zoom in on the first 1 second and the two octaves above concert A xmin = 0; xmax = 1; xlim([xmin xmax]) ymin = 0; ymax = 2; ylim([ymin ymax]) % Add dotted lines showing frequency intervals centered on particular % notes of the musical scale. hold on plot([xmin xmax], (floor(ymin*12)+0.5:ceil(ymax*12)-0.5)'*[1 1]/12, 'w--') hold off note = ['A ';'Bb';'B ';'C ';'Db';'D ';'Eb';'E ';'F ';'Gb';'G ';'Ab']; text(0.95*xmax+0.05*xmin+zeros(1,24),(0:23)/12,[note;note],'Color','w')